About Treatment
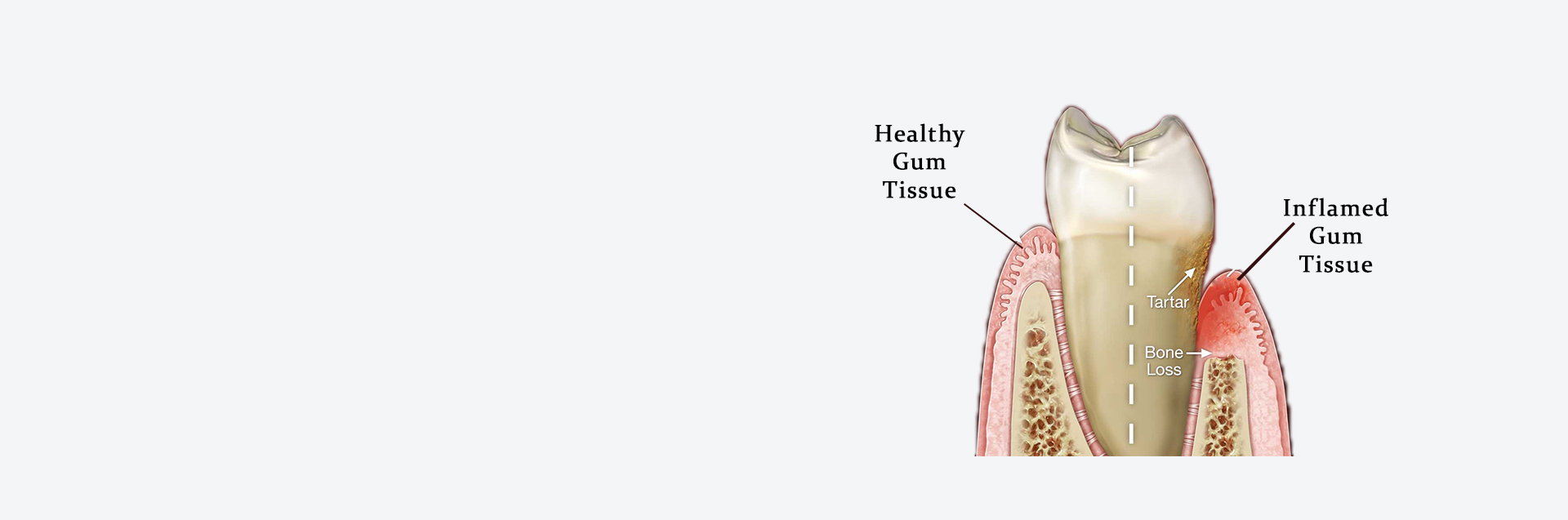
A serious gum infection that damages gums and can destroy the jawbone. Periodontitis is common but fairly preventable. The cause is usually poor oral hygiene. Periodontitis can lead to tooth loss. It's a risk factor for heart and lung diseases.
Periodontitis (Pyorrhoea) (Gum Disease)
Symptoms:
- Swollen, red and tender gums.
- Mouth: bad breath, toothache, bright red gums, loose teeth, receding gums, tender gums, or tooth loss.
- Also common: swelling or bleeding.
Complications
Periodontitis can cause tooth loss. And some research suggests that the bacteria responsible for periodontitis can enter your bloodstream through gum tissue, possibly affecting your heart, lungs and other parts of your body. For example, periodontitis may be linked with respiratory disease, rheumatoid arthritis, coronary artery disease or stroke. But more studies are needed to confirm a link.
Prevention
The best way to prevent periodontitis is to follow a program of good oral hygiene, one that you begin early and practice consistently throughout life.
- Good oral hygiene- That means brushing your teeth for two minutes at least twice daily in the morning and before going to bed and flossing at least once a day. Flossing before you brush allows you to clean away the loosened food particles and bacteria.
- Regular dental visits- See your dentist or dental hygienist regularly for cleanings, usually every 6 to 12 months.
- If you have risk factors that increase your chance of developing periodontitis such as having dry mouth, taking certain medications or smoking you may need professional cleaning more often.
Treatment:
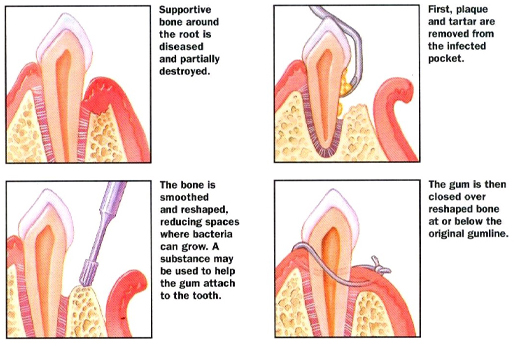
Treatment includes professionally cleaning the pockets around teeth to prevent damage to surrounding bone. Advanced cases may require Surgery.
- Flap surgery (pocket reduction surgery) - Your periodontist makes tiny incisions in your gum so that a section of gum tissue can be lifted back, exposing the roots for more effective scaling and root planing. Because periodontitis often causes bone loss, the underlying bone may be recontoured before the gum tissue is sutured back in place. After you heal, it's easier to clean these areas and maintain healthy gum tissue.
- Soft tissue grafts - When you lose gum tissue, your gumline recedes. You may need to have some of the damaged soft tissue reinforced. This is usually done by removing a small amount of tissue from the roof of your mouth (palate) or another donor source and attaching it to the affected site. This can help reduce further gum recession, cover exposed roots and give your teeth a more pleasing appearance.
- Bone grafting - This procedure is performed when periodontitis has destroyed the bone surrounding your tooth root. The graft may be composed of small fragments of your own bone, or the bone may be synthetic or donated. The bone graft helps prevent tooth loss by holding your tooth in place. It also serves as a platform for the regrowth of natural bone.
- Guided tissue regeneration - This allows the regrowth of bone that was destroyed by bacteria. In one approach, your dentist places a special piece of biocompatible fabric between existing bone and your tooth. The material prevents unwanted tissue from entering the healing area, allowing bone to grow back instead.
- Tissue-stimulating proteins - Another technique involves applying a special gel to a diseased tooth root. This gel contains the same proteins found in developing tooth enamel and stimulates the growth of healthy bone and tissue.
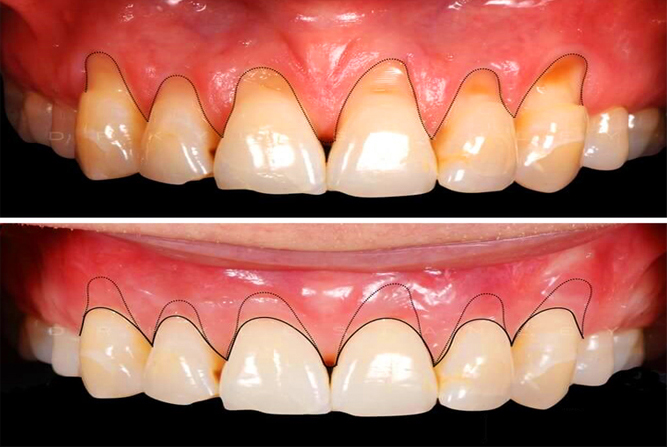
Gum Depigmentation
Gum depigmentation, also known as gum bleaching, is a procedure used in cosmetic dentistry to lighten or remove black spots or patches on the gums consisting of melanin. Different techniques for depigmentation include:
- Scalpel technique.
- Laser.
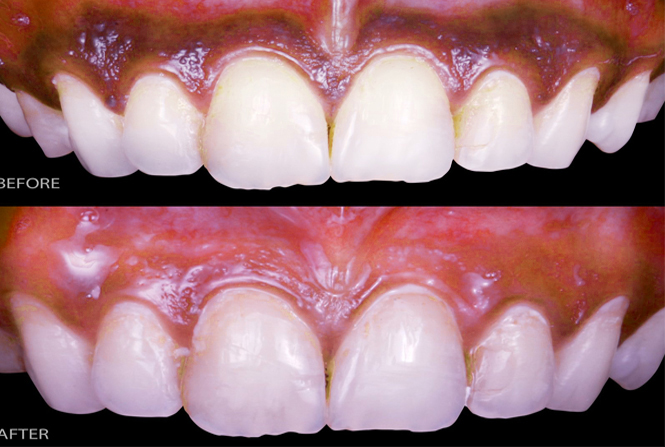
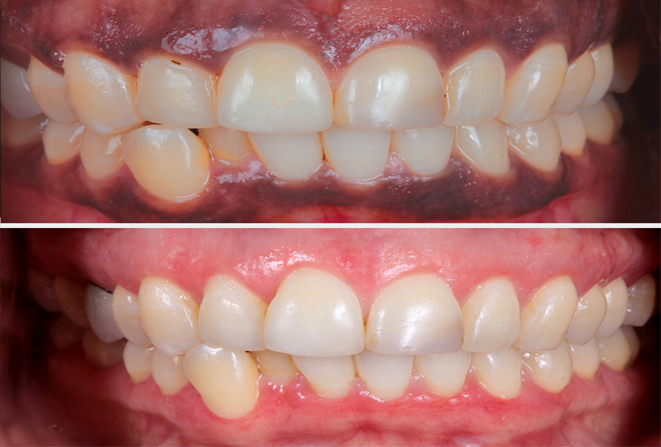
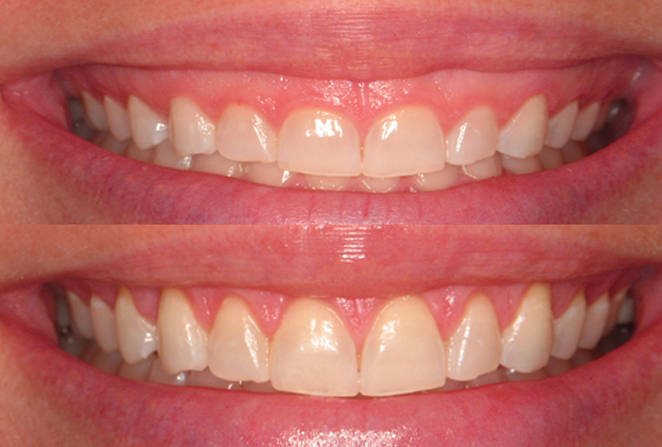
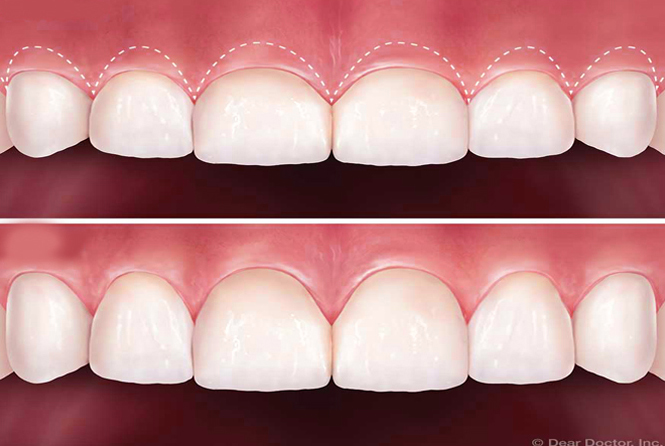
Gummy Smile
Gummy smile also known as excessive gingival display is a smile that shows an excessive amount of gum under the upper lip. It is a common unaesthetic clinical condition, which can be caused by an abnormal dental eruption (delayed passive eruption), or hyperfunction of the upper lip elevator muscle or by an excessive vertical growth of the bone of maxilla or over-eruption of the maxillary anterior teeth, or a combination to one of the above described factors together.
Depending on the severity or the cause of the condition, different options are available. A laser gum lift can improve the appearance. Also, a lot of times a gummy smile develops from the way the jaw has developed. That can be corrected in a non-invasive way with remolding the bone with specific method of orthodontic therapy.
How Are Gummy Smiles Treated?
- Lip repositioning - If the lips are the issue, they can be adjusted to reveal less of a person's gums.
- Laser treatment - This is a common option for patients when the gum tissue is the problem.
- Braces (Orthodontic Treatment).